BAND SAW BLADES
Band saw blades are produced from diffrent materials such M42 to guarantee the highest performances while cutting all kind of materials normally used in mechanic workings. We can be supplied with different toothings according to customer needs.
Our quality standards continue to distinguish the precision bandsaw blades we produce for our partners all over the world. In order to actively maintain this high quality standard. our company has been certified according to the DIN EN ISO 9001:2015 quality management system since 1995.
MULTICUT
For cutting all usual types of steel up to a hardness of 45 HRc.

Our solution for:
• Single, layer and bundle cuts
• K-tooth: Sawing solid material
Advantages:
• Robust bandsaw blade with long service life
• Optimal for standard to high-alloyed materials
• Low noise level due to reduced vibrations
DUROCUT MASTER
Universal heavy duty blade designed for large cross sections also on lower alloyed steel grades.

Our solution for:
• Medium-size to large workpieces
• Thick-walled pipes
• Materials with tensile strength over 1400 N/mm2
• For materials WITHOUT residual stress
Advantages:
• Extended service life
• Lower cutting costs
• Heat resistance and wear resistance
• Fine to very fine cutting surface
• Reduced cutting channel compared to CrNiCut
PROBEAM
Tubes, beams and structurals

Our solution for:
• Profiles and beams
• Single, layer and bundle cuts for pipes and beams in
general steel construction and manufacturing industry
Advantages:
• No binding in the cutting channel
• Minimal tooth chipping, extremely long service life
• Vibration resistance
• Optimal surface quality
-

Alucut(Bimetal Sawblade M42)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

CrNiCut(Bimetal Sawblade M51)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

DUROCUT MASTER ( Bimetal Bandsaw Blades PM55 PREMIUM )
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Durocut(Bimetal Sawblade M51)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Multicut(Bimetal Sawblade M42)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Nirocut(Bimetal Sawblade M42)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Powercut I Black(TCT Bandsaw Blade)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Powercut I(TCT Bandsaw Blade)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Powercut II A/B(TCT Bandsaw Blade)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Powercut III(TCT Bandsaw Blade)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Probeam(Bimetal Sawblade M42)
อ่านเพิ่ม -

Procut(Bimetal Sawblade M42)
อ่านเพิ่ม
Tooth Types
Band saw blades To obtain optimum cutting ra- tes, tooth pitch and tooth design are of great importance, We offer various tooth pitches to solve your cutting problems.
Type M

This tooth type has ground tooth tips with a chamfered, non-set precutter and two set nishing cutters and is
generally manufactured with a positive rake angle. Its particular tooth
geometry allows economic cutting
of high and highest alloyed steels with bimetal bandsaw blades.
Type N
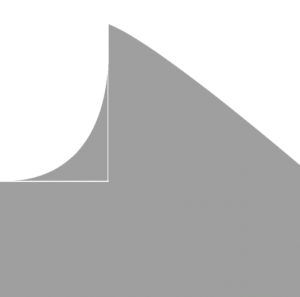
With a rake angle of 0°, this tooth type is particularly suited for cutting short chipping, low alloyed materials, solids in small and medium cross sections as well as tubes and pro les.
Type K/K+

With a positive rake angle of 10° or 16° (K+), the hook tooth has a large, long-drawn-out chip space. Therefore, it is mostly used for cutting non-ferrous metals, steels with a low content of carbon, Cr-Ni alloys, and primarily bigger cross sections.
Type P

The pro le tooth has a special geometry for a vibration-low cutting of beams, structurals and tubes.
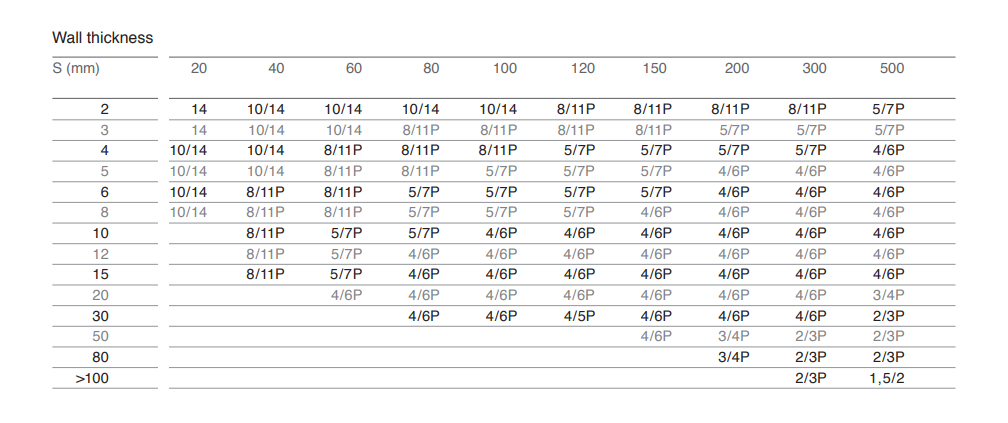
Tooth pitch recommendation Solid Material
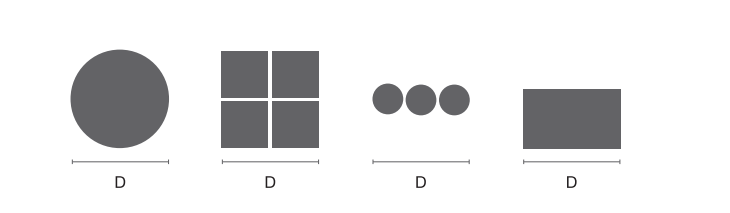
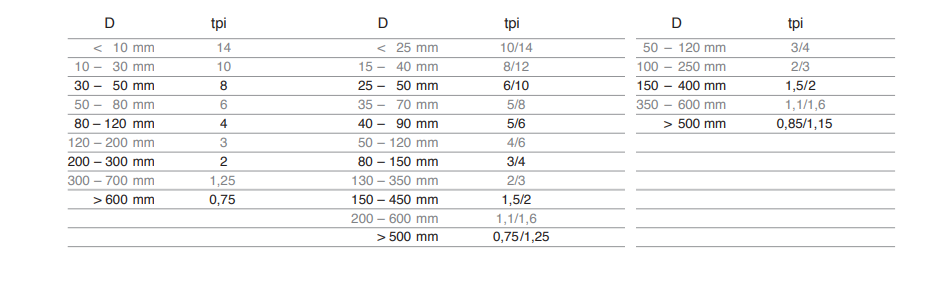
Tooth pitch recommendation Tubes and Profiles
POSSIBLE FAILURE CAUSES
PROBLEM
a) No clearance between body
back and flange of the wheels.
b) Worn back guides
SOLUTION
a) Adjust wheels.
b) Replace back guides.
PROBLEM
Body cracks caused by worn
back guides. Leading to the
back edge of the blade
becoming brittle.
SOLUTION
Replace back guides.
PROBLEM
Worn or incorrectly adjusted
brushes are reducing the life of
the saw blade.
SOLUTION
Adjust brushes regularly and
replace when worn.
PROBLEM
Incorrect alignment causes
burrs at the band back edge,
followed by microcracks.
Result: Blade breakage.
SOLUTION
Adjust wheels. Keep a
clearance between band back
edge and flange of the wheels.
(Recommended clearance:
0.5 to 1.5mm).
PROBLEM
The constant rubbing along the
band saw back edge has
induced a brittleness.
Microcracks appear.
RESULT: Blade breakage
SOLUTION
Replace back guides.
PROBLEM
Too tight or blocked
damping rollers may lead to
rupture of the body.
SOLUTION
Reduce the contact
pressure so the rollers can
be rotated with little effort in
passive state. Replace
blocked damping rollers.
PROBLEM
Too strongly adjusted or
damaged side guides cause
formation of microcracks and
blade breakage.
SOLUTION
Reduce pressure.
Clean side guides.
PROBLEM
The tooth gullet is too small.
To much frictional heat is generated.
Result: Heavy wear and cut deviation.
SOLUTION
Select a coarser tooth pitch
PROBLEM
The tooth gullet is too small.
Chips will overfill the tooth gullet
and lift the blade. When the chip
clears the gullet, the blade will
be forced back into the cutting
channel resulting in a shock load
on the tooth. Leading to tooth
damage.
SOLUTION
Select a coarser tooth pitch
PROBLEM
Teeth have no guide in the
cutting channel. Resulting in
high tooth loads at the cutting
point. Result: Fractures and
breakages as well as
microcracks in the tooth gullet.
SOLUTION
Use finer tooth pitch.

 ไทย
ไทย